How Fraudsters Use Bots to Bypass CAPTCHAs
Sanja Trajcheva
|Cyber Risks & Threats | July 01, 2023

For attackers looking to access your website, a basic security test called CAPTCHA has been the first line of defense since its creation in 2000. In the decades since its inception, CAPTCHA has been the go-to method for stopping bots and keeping websites safe.
But all those years of service on bots and hackers means that bad actors have had a lot of practice getting past these challenges. As a result, CAPTCHAs are now both less effective at blocking bots and more difficult for actual humans to complete.
Now, according to research, half of all CAPTCHAs passed are completed by bots, not real users. That means the attackers controlling the bots can do everything from leaving spam comments and submitting invalid forms to abusing other services that your website provides.
In light of this, now’s a good time to understand how CAPTCHA works, how a CAPTCHA solver can bypass it so easily, and what it means for your website.
What exactly is CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA is a descriptive acronym, and it stands for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart. The goal of the CAPTCHA test is to allow human users to access a website while keeping bots out. CAPTCHA guards everything, from spammy blog comments to even unauthorized downloads.
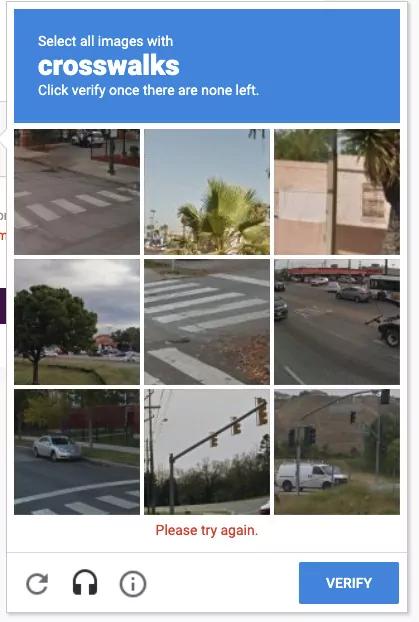
CAPTCHA tests take many forms, but the most popular kind will typically show the users images that are supposedly unreadable by bots. For example, a CAPTCHA may display a series of misshapen or washed-out letters and ask the user to write down the displayed code or may ask the user to identify a set of images that have been distorted in a manner that makes it harder for bots to use OCR.
Users need to input what they see into the provided field, and if they answer correctly, they are granted access to the protected web area. The more simple bots will return irregular and incomprehensible letters or click the wrong images, making it obvious that they are not human.
Advanced bots, on the other hand, can use a variety of strategies to read these distorted images and bypass the test easily. As a result, more sophisticated CAPTCHAs, like reCAPTCHA and hCAPTCHA, have been developed with even more complex puzzles to fight growing bot capabilities.
Why is CAPTCHA used?
CAPTCHA is used by any website that wants to restrict access from bots. The use of CAPTCHAs is widespread–over 30 million websites use reCAPTCHA alone–and the tests are typically placed at gate points in the user experience, such as a download or account creation form, a ticketing system, or a comments section.
CAPTCHAs help businesses filter out potential spam comments, ticket inflation, or even account takeover attacks from malicious bots.
Types of CAPTCHA
CAPTCHA is either text-based, picture-based, or sound-based, and the odds are that you’ve encountered all three.
Text CAPTCHAs
These are the most common, and they require you to look at the distorted text to identify the real message. Sometimes they are actual words, and other times, they are plain gibberish distorted by shape, size, capitalization, or orientation.
The idea behind these wavy text images is to disrupt the way that computers ‘read’ images by breaking up any patterns that programs may have been trained to recognize as text. Think of it as camouflage for words.
If you fail enough text CAPTCHAs, you’ll usually get a prompt to attempt a different method of verification, like a CAPTCHA image.
Picture CAPTCHAs
Image recognition-based CAPTCHA is another commonly used test that prompts the user to prove their humanity by correctly identifying sets of images or portions of a single image. ‘Click every tile with a crosswalk’ or ‘click every image containing a school bus’ are examples. Computers have great difficulty detecting objects in images, and that kind of capability is hard to build and usually out-of-reach for botnets, so image CAPTCHAs are usually effective at keeping out bots. But while they do their job well, they’re also cumbersome and annoying for real users and can cause friction and even abandonment in the customer journey.
A CAPTCHA image can be quite troublesome when it doesn’t look like there’s a clear answer. A great example is a picture where you have to select all the grids with traffic lights, even though the light is split between two grids.
Luckily, you can always hit the refresh button to get another image with zero consequences. Or, you could try the audio CAPTCHA.
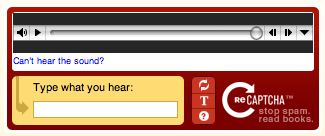
Audio CAPTCHA
With audio CAPTCHAs, users can listen to a short recording and type the word they hear. These are effective because bots can’t use speech recognition to differentiate the pronounced characters from the background noise in the recording. This can be time-consuming, especially compared to a text-based CAPTCHA, and can negatively affect both user experience and page-load times but audio CAPTCHAs are quite effective.
Behavior-based CAPTCHA: reCAPTCHA and hCAPTCHA
As bots have become more advanced, CAPTCHA has needed to add more complex functionality than simple tests and puzzles Enter behavior-based CAPTCHAs, such as Google reCAPTCHA and its primary competitor, hCAPTCHA.
These behavior-based CAPTCHA tools examine identifiers and behavioral data– i.e. how a user interacts with a webpage– to make a decision on their humanity. The classic example is reCAPTCHA’s “I’m not a robot” check box, which tracks mouse movements and other patterns to evaluate users. If reCAPTCHA believes a user is human, they are presented with the simple checkbox test, but if they are believed to be a bot they may be presented with a more difficult image-based test.
By providing different tests based on contextual clues, these tools aim to reduce the friction CAPTCHA places on user experience while still providing tough verification for suspicious users.

However, these tools are still susceptible to advanced bots, or CAPTCHA-solving services, and they come with their own set of difficulties.
Google’s offering, for example, can cause privacy headaches. ReCAPTCHA gathers a lot of device, software, and behavioral data, some of which may be used for purposes beyond security. After all, Google is an advertising company. To drive that point home, earlier this year the French Privacy Commission (CNIL) ruled that reCAPTCHA does not automatically comply with data sharing rules of the GDPR and that user consent must be granted before loading the tool.
For its part, hCAPTCHA does not rely so much on user data, but as a result, it is more likely to present human users with complex challenges which can be quite frustrating, adding an undesirable amount of friction to a landing page.
How do CAPTCHAs affect user experience?
The clear benefit of CAPTCHA is that it is an effective technique to keep common, simple bots off of websites, but there are some major drawbacks to CAPTCHA use, particularly in how they affect real human users.
CAPTCHAs–especially difficult CAPTCHAs–can be very disruptive to user experience and may be difficult for certain audiences to use or understand, resulting in a high rate of false positives and page abandonment.
CAPTCHAs are particularly disruptive for mobile users, who are much more likely to leave a website when challenged than a desktop user.
How do hackers bypass CAPTCHA?
Hackers now have an easier time bypassing normal CAPTCHA challenges, and here are some of the strategies they use.
AI
In his book, Deep Learning for Computer Vision with Python, Adrain Rosebrock lays out his strategy for bypassing CAPTCHA on the E-ZPass New York website. His approach included downloading hundreds of example images to train his system because he didn’t have access to the source code and then releasing the learned AI on the system.
CAPTCHAs with an open source code are, in theory, easier to crack because hackers can use the source to train their machine learning system to bypass CAPTCHA tests, regardless of the difficulty. Anybody can pass the exam if you know all the possible questions.
CAPTCHA hacking strategies
Hack Tricks lists some of the ways that hackers get around CAPTCHA easily. Some of them include checking your page’s source code for CAPTCHA solutions (in case it’s text) or using an old CAPTCHA value in case they get the same challenge twice.
Other CAPTCHA bypass strategies include:
- Using optical character recognition (OCR) to read the characters on the screen
- Checking how many images are being used and detecting them with MD5
- Sending the CAPTCHA parameter empty and seeing if that does the trick.
Browser Extensions and APIs
Browser extensions such as Buster are marketed as tools to help human users solve annoying or difficult CAPTCHA verification challenges, but they can easily be leveraged by bots. Even innocuous APIs can be used, for example, Google’s reCAPTCHA allows users to download audio files, which can then be solved with Google’s own Speech Recognition API!
CAPTCHA solving services and click farms
For hackers who don’t want to develop their own solutions for CAPTCHA challenges, there are a plethora of solutions available that will help them bypass checks for astonishingly low costs. These CAPTCHA services range from APIs leveraging sophisticated AI tools, such as Death By Captcha, which charges $1,39 per 1000 solved CAPTCHA, to click farms that hire large numbers of human workers to manually solve CAPTCHA challenges. These ‘CAPTCHA Farms’ leverage simple APIs that allow a client bot to call the service when it encounters a CAPTCHA, and the workers then solve the CAPTCHA and deliver the response token back to the bot, which enters it and continues its attack.
Pricing for leading vendors such as 2Captcha is around $0.77 per 1,000 Captchas, and the services offer 24/7 availability with thousands of workers available at any time.
These services offer the added benefit of cutting costs for hackers by reducing the infrastructure costs related to spinning up computational resources for complex bots; instead, attackers can leverage simple, lightweight bots and call in help as needed.
Security Bugs
In 2018, a security researcher found a bug that allowed him to bypass Google’s reCAPTCHA. The basic gist is that web apps using reCAPTCHA have to create the request in a specific way, and sometimes, the request is insecure. When this happened, attackers could bypass the reCAPTCHA every single time. (Andres Riancho)
The bug has since been patched, and it’s no longer possible to recreate the reCAPTCHA bypass. However, this is a prime example of how attackers can exploit bugs and weaknesses to bypass your site’s CAPTCHA.
What happens when hackers crack your CAPTCHA?
Any independent hacker can get past your CAPTCHA by simply filling it as a human would. The danger rises when they are able to bypass your CAPTCHA with bots. That means they can bombard your server with many requests, overload your resources, or possibly, steal your data.
Increased spam
Without an effective CAPTCHA “gatekeeper,” you can expect spam comments that advertise everything from malicious services to other websites. If your website is set to approve comments first, they won’t appear to the general public. However, you’ll be drowned by dozens or even hundreds of irrelevant comments on the backend.
Invalid analytics data
Bots will skew the traffic on your web page and render your analytic data useless. If hackers figure out a way to get past your CAPTCHA, you may notice a spike in traffic with zero conversions or find that users are abandoning their carts, and you won’t be able to figure out why.
Insecure shopping checkout
If you own an eCommerce website, a bypassed CAPTCHA means that hackers can now access user accounts, make purchases with stolen cards, and even access other sensitive areas of your website.
Database access
If you don’t have CAPTCHA set up for your website login, then you might want to consider adding it. Bots can be used to access poorly secured user accounts and perform account takeovers. They can also access your online databases and even perform other forms of content-based fraud on your site.
Fewer web resources
With access to your website, bots will bombard your website, submitting connection requests and taking up finite resources. That means that legitimate users will have slowed or even nonexistent access to your website, which can be damaging to your business. Statistics show that 53% of people will go to a competitor if your website takes longer than 3 seconds to load (Digital).
What can you do about CAPTCHA bypassing bots?
Bot Mitigation by CHEQ Essentials
CHEQ Essentials’ bot mitigation adds an additional layer of security to your website, stopping the most common forms of automated traffic from accessing your site. The service scans your visitor activity for telltale signs of bot presence and blocks them from interacting with your website.
That means even if they get through your CAPTCHA, a bot mitigation solution will identify and purge them from your website, allowing only genuine customers to get through.
The bottom line
Hacker tactics are becoming more sophisticated as they get better at bypassing simple defense systems like CAPTCHA, but luckily, you also have access to advanced measures.
CHEQ Essentials will make sure those automated programs don’t bypass CAPTCHAs or mess with your marketing channels or forms. Currently, Bot Zapping works with WordPress sites only.